At The Equilibrium Price / Supply Demand Market Equilibrium Ap Ib College Reviewecon Com - Technically, at this price, the quantity demanded by the buyers is …
Evidently, at the equilibrium price, both buyers and sellers are in a state of no change. At equilibrium, there is neither scarcity nor state of abundance unless there is a change in the elements of demand and supply. Technically, at this price, the quantity demanded by the buyers is … 19.10.2021 · at the equilibrium price, resources are not wasted and consumers have enough goods and services. The results of quantity demanded being greater than quantity supplied.
A legally determine minimum price that sellers may.
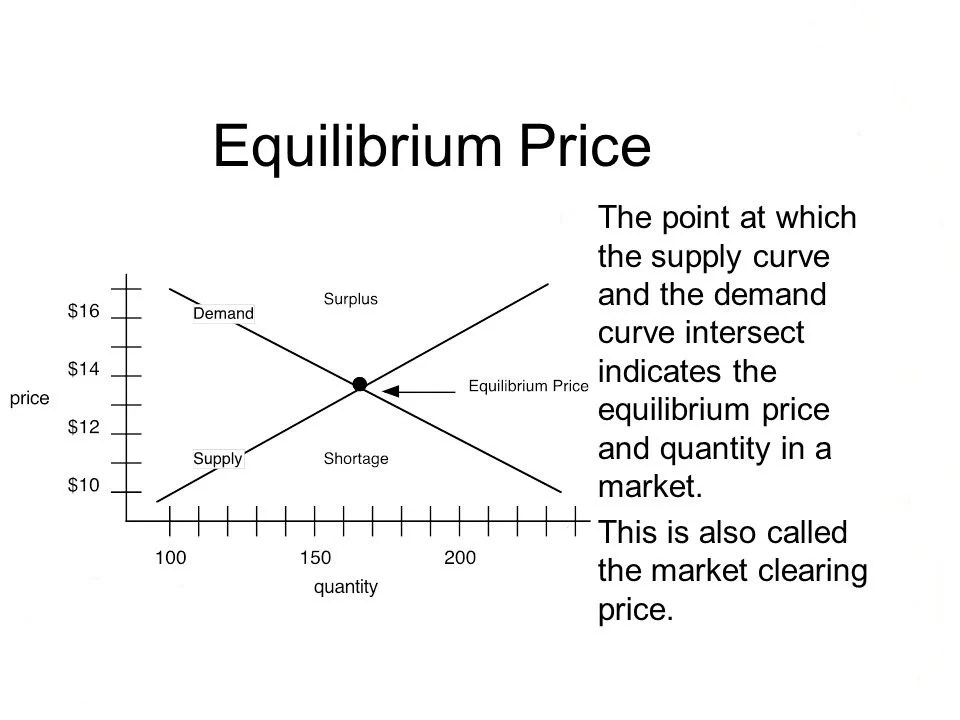
The answer is the equilibrium price. Price at which the quantity of a product demanded by consumers and the quantity supplied by producers are equal. Technically, at this price, the quantity demanded by the buyers is … 05.05.2015 · the equilibrium price is the price at which the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. Equilibrium price is the price where the demand for a product or a service is equal to the supply of the product or service. 19.10.2021 · at the equilibrium price, resources are not wasted and consumers have enough goods and services. At equilibrium, there is neither scarcity nor state of abundance unless there is a change in the elements of demand and supply. At equilibrium level of output ox, price is equal to its marginal cost and marginal cost curve cuts the mr curve from below. Equilibrium means a state of no change. A result of quantity supplied being greater than quantity demanded, usually because prices are too high. What does equilibrium price mean? Graphically, it is the point at which the two curves intersect. At eq, there is no shortage.
The firm enjoys normal profits. Use the basic rules of algebraic equations to solve for p, or the price. Define equilibrium price the price where demand and supply are equal and so there are no surpluses or shortages of the product. Evidently, at the equilibrium price, both buyers and sellers are in a state of no change. At equilibrium level of output ox, price is equal to its marginal cost and marginal cost curve cuts the mr curve from below.

Use the basic rules of algebraic equations to solve for p, or the price.
19.10.2021 · at the equilibrium price, resources are not wasted and consumers have enough goods and services. A legally determine minimum price that sellers may. At equilibrium, both consumers and producers are satisfied, thereby keeping the price of the product or the service stable. A result of quantity supplied being greater than quantity demanded, usually because prices are too high. Now, suppose demand increases from dd to d 1 d 1 and the industry is in equilibrium at point e 1 which determines the price op 1 the new price op 1 is less than the new market price i.e., oh. 05.05.2015 · the equilibrium price is the price at which the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. The firm enjoys normal profits. What is another term for equilibrium price Let us take a look. Use the basic rules of algebraic equations to solve for p, or the price. At eq, there is no shortage. Evidently, at the equilibrium price, both buyers and sellers are in a state of no change. The results of quantity demanded being greater than quantity supplied.
Graphically, it is the point at which the two curves intersect. Evidently, at the equilibrium price, both buyers and sellers are in a state of no change. 05.05.2015 · the equilibrium price is the price at which the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. At eq, there is no shortage. Define equilibrium price the price where demand and supply are equal and so there are no surpluses or shortages of the product.

The answer is the equilibrium price.
At equilibrium, both consumers and producers are satisfied, thereby keeping the price of the product or the service stable. At equilibrium, there is neither scarcity nor state of abundance unless there is a change in the elements of demand and supply. What does equilibrium price mean? Technically, at this price, the quantity demanded by the buyers is … Equilibrium means a state of no change. With the increase or decrease in demand and supply, inverse behaviour occurs. A result of quantity supplied being greater than quantity demanded, usually because prices are too high. At eq, there is no shortage. 05.05.2015 · the equilibrium price is the price at which the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. What is another term for equilibrium price Let us take a look. A legally determine minimum price that sellers may. Equilibrium price definition can be understood this way, the neutral point of price where both the buyers and sellers are satisfied.
At The Equilibrium Price / Supply Demand Market Equilibrium Ap Ib College Reviewecon Com - Technically, at this price, the quantity demanded by the buyers is …. At equilibrium level of output ox, price is equal to its marginal cost and marginal cost curve cuts the mr curve from below. A result of quantity supplied being greater than quantity demanded, usually because prices are too high. At equilibrium, both consumers and producers are satisfied, thereby keeping the price of the product or the service stable. Use the basic rules of algebraic equations to solve for p, or the price. 08.03.2021 · solve for the equilibrium price.
At equilibrium, there is neither scarcity nor state of abundance unless there is a change in the elements of demand and supply at the equilibrium. The results of quantity demanded being greater than quantity supplied.